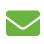
"The Abbey Ruins" Bury St Edmunds
The first religious foundation there was established by Sigebert, King of the East Angles, who resigned his crown to found a monastery about 537. It became celebrated when the relics of the martyred King Edmund were brought there in 903, after which time the town, till then called Boedericsworth, became known as St. Edmund's Town or St. Edmund's Bury. During the reign of Canute (1016-35) the secular canons were replaced by Benedictines. In 1095 there was a solemn translation of the saint's relics to the new church built by Abbot Baldwin. At the beginning of the 12th Century, a second church, St James, was built within the grounds. The shrine grew in fame, wealth, and magnificence till the monastery was considered second only to Glastonbury, but in 1465 a terrible fire caused irreparable loss to the church, from which it never recovered. The abbot had a seat in Parliament and possessed full jurisdiction over the town and neighbourhood. There was accomodation for eighty monks, but more than two hundred persons resided in the Abbey. It was in the abbey church that the memorable meeting of barons took place in the year 1214, when Cardinal Langton, Archbishop of Canterbury, standing at the high altar, read out the proposed Charter of Liberties, which in the form of Magna Charta was signed by King John in 1215. The abbey was finally dissolved by Henry VIII in 1539, when the abbey church and the monastic buildings were in large measure destroyed, the gateway, an ancient bridge, and other scattered ruins alone now remaining. With the arrival of the new Millennium, work began on a Gothic revival tower for the Cathedral (previously known as St James), created by local craftsmen using traditional materials and methods, and opened in 2005, this is the tower that can be seen in the photograph.
- 0
- 1
- Panasonic DMC-FS10
- 1/100
- f/9.0
- 5mm
- 200

Comments
Sign in or get an account to comment.